09 February, 2026
Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY): 11 Years Completed
Fri 29 Aug, 2025
Reference:
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) completed its eleventh year on 28 August 2025.
Key Points:
- During this period, it has played a significant role in transforming India’s financial landscape.
Achievements:
- As of 13 August 2025, total PMJDY accounts: 561.6 million
- 55.7% (313.1 million) of PMJDY account holders are women, and 66.7% (374.8 million) accounts are in rural and semi-urban areas.
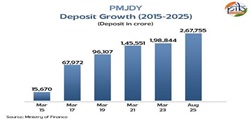
Deposits in Accounts (as of 13 August 2025):
- Total: ₹2,67,756 crore
- The number of accounts has tripled, while total deposits have increased nearly 12 times.
Average Deposit per Account (as of 13 August 2025):
- Average deposit per account: ₹4,768
- Compared to August 2015, average deposit per account increased 3.7 times.
- The rise in average deposits indicates increased account usage and development of savings habits among account holders.
Rupee Cards Issued (as of 13 August 2025):
- Total Rupee Cards issued: 386.8 million
- The number and usage of Rupee Cards have increased over time.
- POS/MPOS Machines: 11.1 million POS/MPOS machines installed nationwide.
Digital Transactions (Total):
- FY 2018-19 → 2,338 crore
- FY 2024-25 → 22,198 crore
- Nearly a 10-fold increase in 6 years.
UPI Transactions:
- FY 2018-19 → 535 crore
- FY 2024-25 → 18,587 crore
- UPI has become the backbone of digital payments.
Rupee Card Transactions (POS & E-Commerce):
- FY 2017-18 → 67 crore
- FY 2024-25 → 93.85 crore
Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY): General Information
| Category | Description |
| Launch | 28 August 2014 |
| Inauguration | Prime Minister Narendra Modi |
| Objectives |
- Connect every household to banking services - Ensure financial inclusion - Provide affordable banking, savings, insurance, and pension services to poor and disadvantaged sections |
| Key Features |
- Zero balance accounts - Rupee debit card (with accident insurance cover) - Life insurance cover (up to ₹30,000) - Overdraft facility (up to ₹10,000) - Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) - Access to pension schemes (Atal Pension Yojana) - Digital banking and UPI services - Micro-induction loan facility (MUDRA) |
| Insurance Cover | Accident insurance up to ₹2 lakh, life insurance up to ₹30,000 |
| Overdraft Facility | Overdraft facility for account holders after 6 months, up to ₹10,000 |
| Beneficiary Level | Linked with beneficiaries of Direct Benefit Transfer schemes |
| Financial Inclusion | Significant role in financial inclusion, especially in rural and backward areas |
| Other Important Points |
- PMJDY accounts do not require maintaining a minimum balance. - Free Rupee debit card is provided to account holders. - The scheme promotes digital transactions. - Ensures access to credit, insurance, and pension services. - PMJDY accounts played a vital role during COVID-19 welfare schemes. |
Other Major Financial Inclusion Schemes
| Scheme Name | Launch Date | Key Features |
| Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY) | April 2015 | Promotes self-employment, provides loans to small and micro-enterprises |
| Atal Pension Yojana (APY) | June 2015 | Stable pension scheme for rural and unorganized sector |
| Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY) | May 2015 | Accident insurance cover up to ₹2 lakh |
| Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY) | May 2015 | Life insurance up to ₹2 lakh |
| Stand Up India Scheme | March 2016 | Stand-up loans for SC/ST, women, and entrepreneurs |
| Financial Literacy Centres (CFL) | 2013 | Financial literacy and awareness campaigns |
| Digital Banking Units (DBUs) | 2022 | Basic banking services, payments, account opening, passbook issuance |