23 February, 2026
Achievements under the National Sickle Cell Mission
Tue 22 Jul, 2025
Reference:
- The National Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission, launched on 1 July 2023 at Shahdol (Madhya Pradesh) by the Hon’ble Prime Minister, has shown remarkable progress so far.
Key Points
Progress So Far (as of July 2025)
| Component | Achievement |
| Target Population | 7 crore people |
| Screened so far | 6 crore people (≈ 86%) |
| Confirmed Patients | 2.15 lakh |
| Sickle Cell Carriers | 16.7 lakh |
| Health Cards Issued | 2.6 crore |
State-wise Highlights
- High-performing states (based on screening %):
Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Telangana, Karnataka, Uttarakhand
- States with the highest number of confirmed cases:
Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Gujarat
Technology and Monitoring System
| Initiative | Description |
| POCT Kits (Point-of-Care Testing) | Certified, rapid, and reliable screening technology |
| Dashboard and Portal | Real-time monitoring and data integration from all states |
National Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission
Launch Details:
- Date: 1 July 2023
- Location: Shahdol, Madhya Pradesh
- Launched by: Hon’ble Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi
Objectives:
- To eliminate sickle cell anaemia from India by 2047
- To conduct universal screening of 7 crore people aged 0 to 40 years
- To provide awareness, counselling, and treatment services in affected tribal regions
Target Year:
- By FY 2025-26: Completion of screening of 7 crore people
- By 2047: Complete elimination of the disease
Major Components:
- Screening
- Counselling
- Treatment
- Awareness Campaigns
- Distribution of Health Cards
- SCD Portal and Digital Dashboard
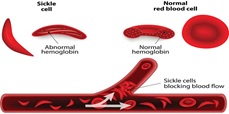
Sickle Cell Anaemia: General Information
- A genetic blood disorder that affects red blood cells
- Primarily affects tribal communities
- In this disease, red blood cells (RBCs) become sickle or crescent-shaped instead of the normal round shape
- This causes blockage of blood flow and disrupts oxygen supply to body organs
Main Causes:
- Hereditary disease passed from parents to children
- A child is affected only if both parents carry the sickle gene
Symptoms:
- Recurrent bone pain
- Fatigue and weakness
- Jaundice
- Shortness of breath
- Delayed growth in children
- Higher susceptibility to infections
Global Context:
- India ranks third globally in sickle cell disease cases, after Nigeria and the Democratic Republic of the Congo